Cassava Production In Nigeria And The Main Producing States

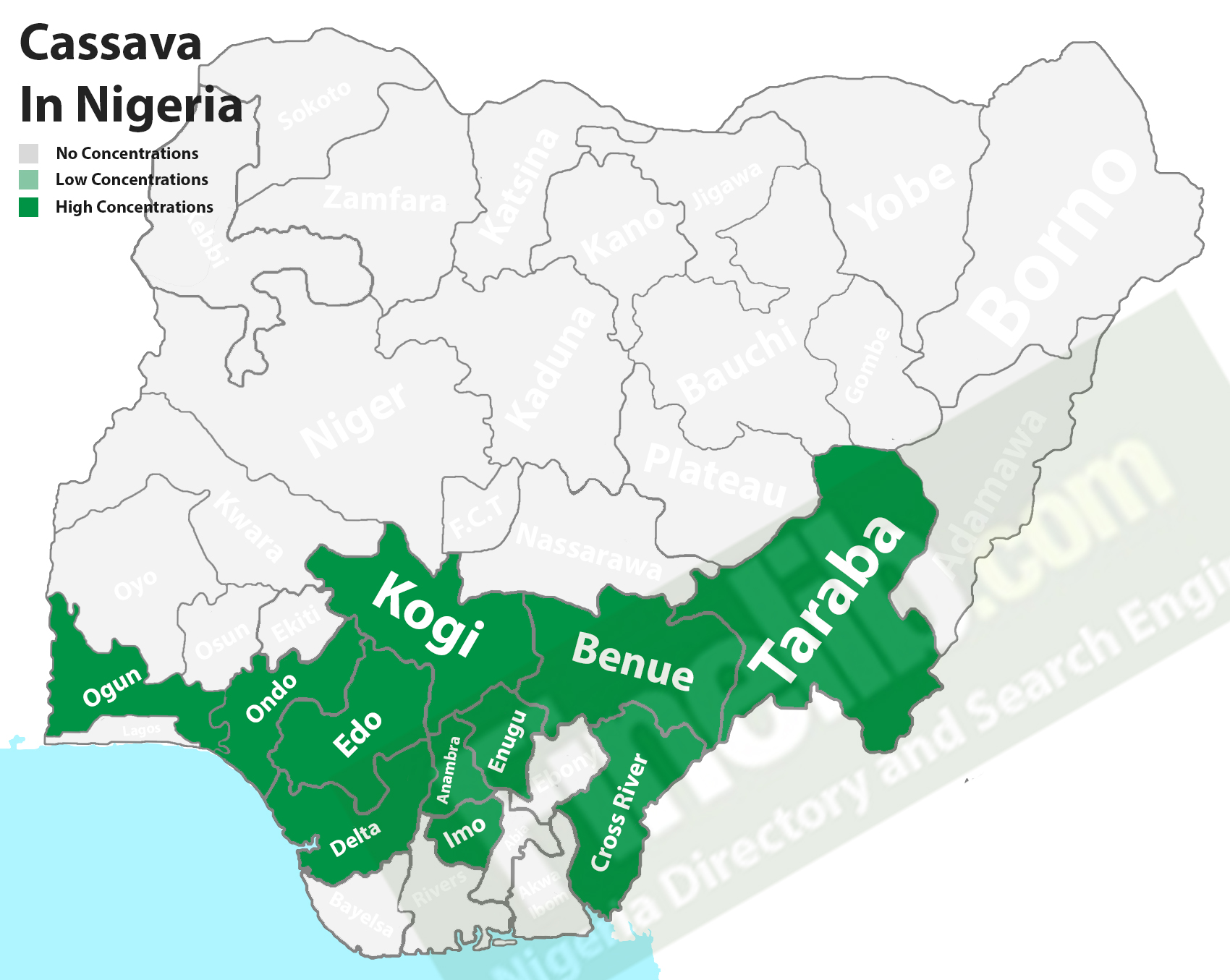
In terms of cassava production, Nigeria which is situated in Western Africa is rated as the world's largest producer of cassava, while in terms of cassava exports, Thailand is rated as the largest exporter of dried cassava. The Main producing states of cassava in Nigeria are; Imo, Anambra, Kogi, Cross River, Enugu, Ogun, Ondo, Taraba, Benue, Delta, and Edo, though it can be cultivated in other states of Nigeria but in smaller quantities.
Of all the continents in the world, Africa is the only one that largely depends on roots and tubers as a major food crop for feeding and this is the reason why root and tubers especially cassava is being grown in various tropical countries of Africa; where about 70% of the food crop is consumed and the remaining exported to other countries.
Cassava called Manihot esculenta (botanical name) is a popular crop of the roots and tubers. It is a perennial crop that grows in tropical and subtropical areas of the world.
It was in the mid-1550s introduced to Africa from by the Portuguese and is today one of the staple foods in the country and other tropical Africa countries.
It is the 3rd largest source of food carbohydrates in the tropics, after rice and maize and is capable of growing on marginal soils because of its drought-tolerant nature.
It is not only rich in carbohydrates, but also contains calcium, vitamins B and C, and essential minerals, though nutrient compositions of the crop are dependent on the age of the harvested crop, soil conditions, climate, and other environmental factors during cultivation.
Cassava undergoes various processes from farming to harvesting and post harvesting handling and storage; in Nigeria, it is one of the most widely cultivated food crops and it is widely eaten by all though processed differently.
It is normally being processed into various products in Nigeria but it can still be stored fresh and the best way to preserve it is by using thiabendazole or maybe bleach with can act as a fungicide after which it is wrapped in plastic and then frozen, it can also be coated in wax if freezing isn’t available.
This way of preserving fresh cassava can then make the exportation of fresh whole cassava abroad possible without any fear of decay by pests, fungi or purified protein derivative (PPD) which has been a major factor affecting cassava after it is separated from the main plant.
Applications of cassava
- Cassava can be processed into starch; the cassava starch can be added to the ingredients for making paper and clothing textiles.
- Cassava can be processed into flour, the cassava flour can be added to expensively imported flour (provided the quality of the cassava flour is good enough) to make cakes, bread, and biscuits.
- Cassava can be processed into chips, Cassava chips can be used for animal feed
- Cassava can be processed into ethanol and the ethanol produced from cassava can be used as biofuel when combined with additives.
- Cassava can be processed into fructose and the fructose is used in industry for sweetening fizzy drinks.
- Cassava can be processed into garri and Fufu.




