Silica (SiO2) Natural Resources Deposits In Nigeria And Its Uses

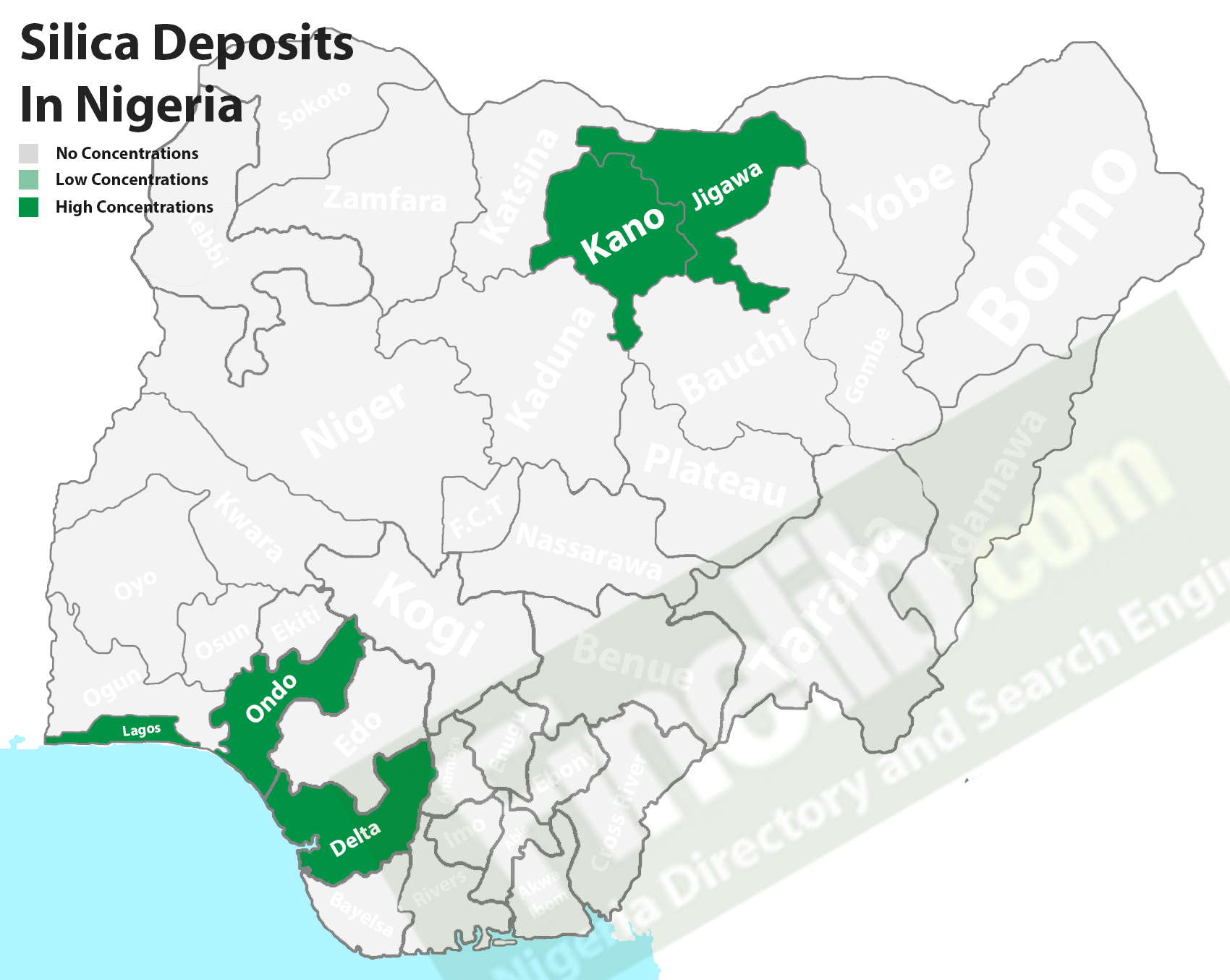
Silica in Nigeria, West Africa can be found in Nigerian states such as Kano, Jigawa, Delta, Lagos, and Ondo.
Silica or Silicon dioxide which can also be called silica sand is another natural resource that can be found in Nigeria, and occurs in compounds with the two most abundant elements in the earth's crust namely; silicon and oxygen.
Silica is also known as silica sand, it is a chemical compound that is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula SiO2 and occurs naturally as quartz (the quartz is broken down into tiny granules by water and wind over a period of time to form silicon) flint, and agate as well as in various living organisms.
Silica is made up of silicon and oxygen in the ratio of 1:2, and is found commonly in the crystalline state and rarely in an amorphous state. The deposit of silica is usually derived by quarrying and then subjected to further processing in order to
a. Make the quartz grains clean and increase the percentage of silica present through washing and scrubbing to remove clay minerals.
b. Produce the right distribution size of the product which is dependent on the end-user and this is achieved by screening out the unwanted particles.
c. Reduce the number of impurities, especially chromium and iron which color glass, these impurities can be removed by the process of froth flotation, gravity separation, and magnetic separation. Hydrofluoric acid combined with thermal shock is used for a higher purity for electronics applications.
The sand may be dried after processing and grounded into fine particles, called silica flour. The quartz may also be melted in electric arc furnaces, cooled, and grounded to produce fused silica.
Silica has been researched to be non-poisonous when it's being taken orally as it has been observed to help reduce the potential risk of getting dementia, but inhaling it is toxic. Crystalline silica when inhaled can seriously lead to many health defects and unhealthy conditions such as lung cancer, silicosis, bronchitis, systemic autoimmune diseases like lupus and rheumatoid arthritis, as the finely divided particles are been trapped or embedded on the walls of the lungs, irritating the tissue continuously thereby decreasing the capacities of the lungs.
Uses of silica
- Used in the food and pharmaceutical industry.
- Used in glass making.
- It is a major component of glass and silicon, used in sand casting and Portland cement.
- Is used as a proppant by companies involved in oil and natural gas recovery.
- In its finest form, it is used as a functional filler for paints, plastics, rubber.
- Silica sand is used in water filtration and agriculture.




